23 Jan 2026
Updated on January 28th, 2026
DevOps Process in Application Development: A Complete Guide
Matthew Connor

In today’s fast-paced software industry, delivering high-quality applications quickly is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. DevOps, a combination of development and operations, has emerged as a methodology that enables teams to build, test, and release applications faster while ensuring quality, stability, and scalability.
This comprehensive guide explores the DevOps process in application development, its benefits, key tools, best practices, and how organizations can leverage DevOps to transform software delivery. Whether you are a startup, an enterprise, or looking for a top DevOps company in the United States, this guide will help you understand why DevOps is a game-changer in modern application development.
What is DevOps in Application Development?
The DevOps process in application development is a set of practices that combines people, processes, and tools to improve collaboration between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). Traditionally, these teams worked separately, leading to slow releases, miscommunication, and operational issues. DevOps removes these barriers and creates a unified workflow focused on speed, quality, and reliability.
DevOps promotes continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), allowing teams to build, test, and deploy applications faster and more frequently. By automating manual tasks and encouraging shared responsibility, DevOps helps organizations respond quickly to market changes and user demands.
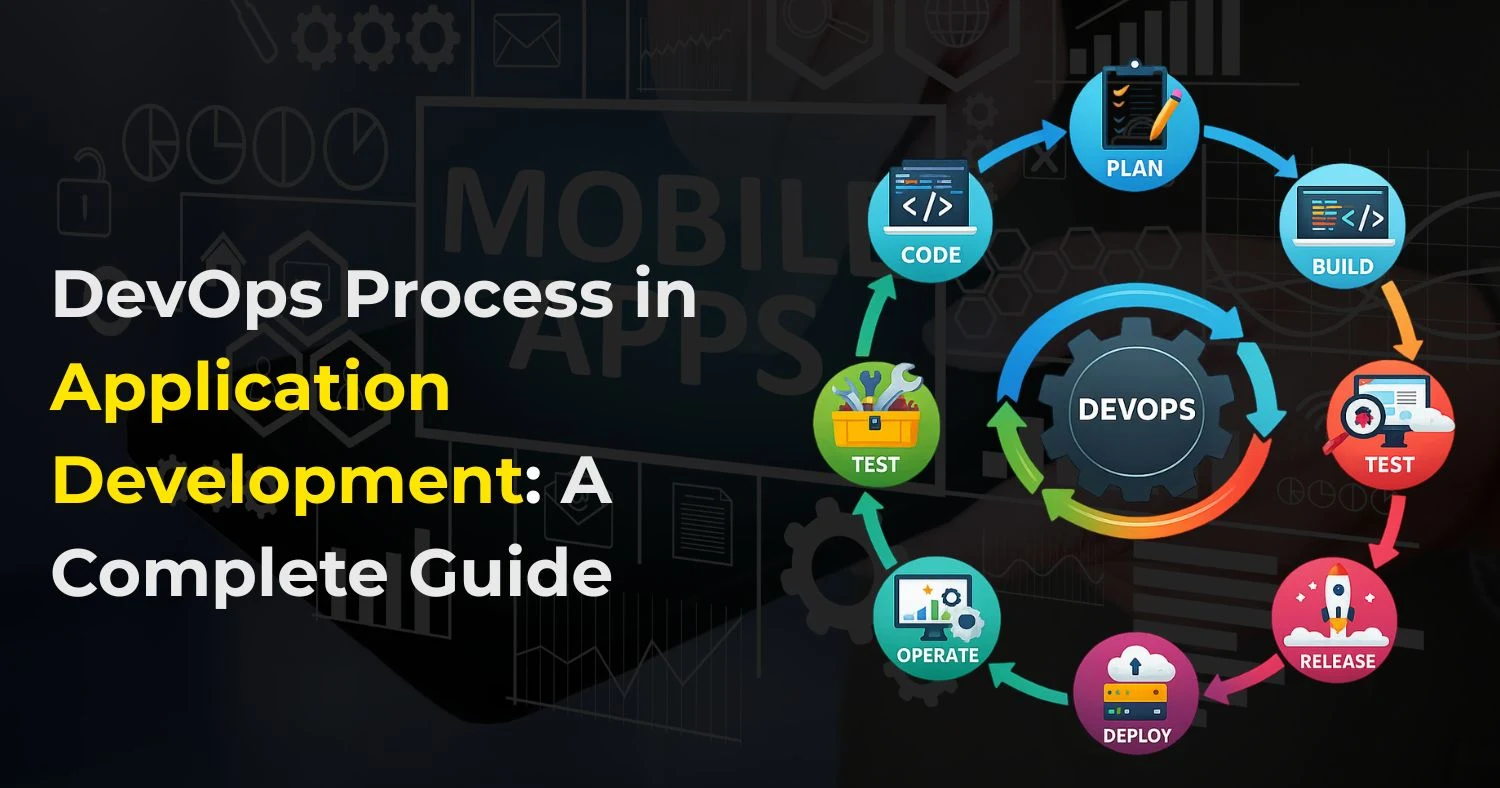
DevOps Lifecycle in Application Development
The DevOps process lifecycle is continuous and iterative, ensuring ongoing improvement and faster delivery. Each stage is interconnected, ensuring continuous integration, delivery, monitoring, and improvement.
Planning
Planning sets the foundation for the entire DevOps lifecycle. It focuses on aligning business goals with technical requirements while preparing teams for smooth execution.
Key activities include:
- Requirement gathering and clear documentation
- Defining project scope, timelines, and milestones
- Resource allocation and team role assignment
- Risk assessment and mitigation planning
- Selecting suitable tools and technologies
Effective planning reduces uncertainties and ensures better collaboration between development and operations teams.
Coding
The coding phase involves developing application features based on planned requirements. DevOps promotes collaborative coding practices to maintain speed and quality.
Best practices include:
- Writing modular, clean, and reusable code
- Using version control systems like Git and Bitbucket
- Performing regular code reviews to improve quality
- Following consistent coding standards across teams
- Integrating code frequently to avoid conflicts
This phase ensures faster development with fewer errors.
Building
During the build phase, source code is compiled, packaged, and prepared for deployment. Automation plays a key role here.
Key points include:
- Automated builds using tools like Jenkins, Bamboo, or Travis CI
- Continuous integration to merge code changes smoothly
- Early identification of build failures and dependency issues
- Faster build cycles for frequent releases
Automated builds help maintain consistency and reliability across environments.
Testing
Testing ensures the application meets quality, performance, and security standards before release. DevOps emphasizes automated testing for faster feedback.
Common testing types include:
- Unit testing to validate individual components
- Integration testing to ensure system compatibility
- Performance testing to handle peak loads
- Security testing to detect vulnerabilities
Tools such as Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG help teams run tests continuously and reduce manual effort.
Deployment
Deployment involves releasing the application to staging or production environments. DevOps supports continuous deployment for faster and safer releases.
Common tools include:
- Docker for containerizing applications
- Kubernetes for container orchestration
- Ansible or Chef for configuration management
Automated deployments reduce downtime and ensure consistent releases.
Monitoring
Monitoring tracks application performance and system health after deployment to ensure stability and reliability.
Key metrics monitored include:
- Application uptime and availability
- Response time and latency
- Error rates and logs
- Security threats or unusual activity
Tools like Nagios, Prometheus, Grafana, and the ELK Stack provide real-time insights and alerts.
Feedback and Optimization
The final stage focuses on collecting feedback from users, monitoring tools, and business teams.
Key activities include:
- Analyzing user behavior and performance data
- Identifying areas for improvement
- Fixing issues and optimizing features
- Planning enhancements for future releases
Continuous feedback ensures the application evolves to meet user expectations and business goals efficiently.
Key Benefits of DevOps in Application Development
Adopting DevOps in application development provides significant advantages for organizations aiming to deliver high-quality software faster and more efficiently. By combining automation, collaboration, and continuous feedback, DevOps transforms the way applications are built, tested, and deployed.
- Faster Time-to-Market: DevOps uses automated CI/CD pipelines to speed up development, testing, and deployment. This allows teams to release new features, updates, and fixes more frequently, helping businesses stay competitive.
- Improved Collaboration: DevOps promotes seamless teamwork by aligning development, operations, and QA teams under shared goals and workflows. With shared responsibilities and clear communication, teams work toward common goals, reducing misunderstandings and delays.
- Enhanced Software Quality: Continuous testing, monitoring, and early bug detection ensure applications are more stable and reliable. Issues are identified early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of failures in production.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation minimizes manual work, lowers error rates, and reduces the need for repetitive tasks. This leads to better use of resources and lower overall development and maintenance costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: DevOps supports seamless scaling of applications and infrastructure. Teams can easily handle increased user demand without performance issues or downtime.
- Continuous Improvement: Real-time monitoring and user feedback provide valuable insights into application performance. Teams can quickly make data-driven improvements to enhance user experience and system efficiency.
By implementing DevOps practices, organizations can achieve faster releases, better collaboration, improved reliability, and long-term application success.
DevOps Tools for Application Development
Implementing DevOps requires a carefully selected set of tools that automate, monitor, and streamline development and operations processes. Using the right tools ensures faster releases, higher-quality applications, and improved collaboration between teams. Key categories include:
- Version Control: Tools like Git, Bitbucket, and GitHub help manage code versions, track changes, and enable multiple developers to work simultaneously without conflicts.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Platforms such as Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI automate builds, testing, and deployment pipelines, ensuring faster and more reliable releases.
- Containerization: Docker and Kubernetes enable packaging applications with all dependencies, ensuring consistency across environments and easier deployment.
- Configuration Management: Tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef automate infrastructure setup and configuration, reducing manual errors.
- Monitoring & Logging: Nagios, Prometheus, Grafana, and the ELK Stack provide real-time monitoring, log aggregation, and alerting to ensure application health and performance.
- Collaboration & Tracking: Platforms such as Jira, Trello, and Slack improve communication, project tracking, and issue resolution across development and operations teams.
Choosing the right DevOps tools depends on your application type, team size, deployment environment, and project requirements. These tools also align with mobile app development trends for faster, more efficient software delivery.
Best Practices for Implementing DevOps
To successfully adopt DevOps, organizations must focus on people, processes, and technology together. Following proven best practices helps teams achieve faster releases, better stability, and long-term success.
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: Begin with a pilot project to test DevOps workflows, tools, and collaboration models. Once the team gains confidence and resolves challenges, scale DevOps practices across other projects.
- Automate Wherever Possible: Automate repetitive tasks such as code builds, testing, deployments, and infrastructure provisioning. Automation reduces manual errors, saves time, and ensures consistent outcomes across environments.
- Encourage Cross-Team Collaboration: Break down silos between development, operations, and QA teams. Shared responsibilities, regular meetings, and transparent communication improve problem-solving and speed up delivery.
- Integrate Security from Day One (DevSecOps): Embed security checks into every stage of the pipeline. Use automated vulnerability scans, access controls, and compliance checks to detect issues early and reduce security risks.
- Monitor Continuously and Proactively: Track application performance, system health, error logs, and user behavior in real time. Continuous monitoring helps teams identify and fix issues before they impact users.
- Embrace Continuous Feedback: Collect feedback from users, monitoring tools, and internal teams. Use these insights to improve performance, usability, and reliability with every release.
DevOps in Cloud-Based Application Development
Cloud computing and DevOps work hand-in-hand. Cloud platforms provide scalable, flexible infrastructure that complements DevOps automation and accelerates delivery.
Benefits of Cloud-Based DevOps include:
- Rapid Provisioning: Quickly set up development, testing, and production environments.
- Scalability and Load Balancing: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Integration with CI/CD Pipelines: Seamlessly integrate automated pipelines for faster deployment cycles.
- Centralized Monitoring and Logging: Aggregate logs and metrics from cloud services for better visibility and proactive issue detection.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based backups and replication improve application resilience and recovery.
Partnering with a Mobile app development company in the USA can ensure cloud DevOps adoption is smooth and aligned with business objectives.
Measuring DevOps Success
Measuring DevOps success helps organizations understand how well their processes, tools, and teams are performing. Tracking the right key performance indicators (KPIs) ensures continuous improvement and better business outcomes.
- Deployment Frequency: Indicates how often new features, updates, or fixes are released. Higher frequency shows efficient automation and faster delivery cycles.
- Lead Time for Changes: Measures the time taken from code commit to production deployment. Shorter lead times reflect smoother CI/CD pipelines and quicker response to market needs.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): Tracks how quickly systems recover from failures or outages. Lower MTTR highlights strong monitoring, alerting, and incident response practices.
- Change Failure Rate: Shows the percentage of deployments that cause issues or require rollbacks. A lower rate indicates stable releases and effective testing.
- Customer Satisfaction: Use user feedback, app ratings, reviews, and Net Promoter Score (NPS) to assess real-world application performance and user experience.
Conclusion
The DevOps process in application development is a comprehensive approach that blends culture, tools, and best practices to deliver high-quality applications faster. By integrating DevOps into their workflows, organizations can improve collaboration, automate repetitive tasks, and ensure continuous delivery of software with fewer errors.



